TCL #48: Consolidation and Critical Minerals
Last week's transactions reveal the contours of American industrial policy in action. The federal government is deploying over $700 million in loans and incentives to establish domestic rare earth magnet production, addressing a critical supply chain vulnerability. Meanwhile, capital continues to consolidate. Oil producers are merging to achieve scale in the Permian Basin, Apollo is writing cheques for European energy infrastructure, and pharmaceutical giants are competing for an obesity drug developer.
Somewhere between these transactions, copper became a matter of national security.
Rare Earths
Vulcan Elements and ReELement Technologies have secured a $1.4 billion partnership with the US Government and private investors to develop a fully vertically integrated, domestic supply chain for rare earth magnets. Vulcan will construct and operate a 10,000 metric tonne magnet facility in US. This expansion of capacity will be financed with a $620 million Direct Loan from the Department of War's Office of Strategic Capital, $50 million in federal incentives from the CHIPS and Science Act, and $550 million in private capital. ReElement will also expand its recycling and processing capabilities with an $80 million Direct Loan from the Office of Strategic Capital, matched by private capital.
The Department of War will acquire warrants in both Vulcan and ReElement. The Department of Commerce will gain $50 million in equity in Vulcan. The two companies maintain an integrated process where ReElement recycles end-of-life magnets and electronic waste into rare earth oxides, and Vulcan converts the oxides into metals and final magnet products, all within the US.
Battery
Xpeng Inc., a Chinese electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer, is planning to integrate solid-state batteries into its new IRON humanoid robot. This technology is being implemented to provide long-lasting energy without overheating, enhancing the robot's safety, efficiency, and performance. The robot also features Xpeng's in-house Turing AI chips and a vision-language-action (VLA) model primarily used in robot learning and embodied AI systems. The company plans to produce its first large batch of robots by the end of 2026 for internal use as salespeople and tour guides.
Mining
Vedanta Resources, a diversified mining and non-ferrous metals company, is transferring its Konkola Copper Mines (KCM) in Zambia to a new US-based subsidiary called CopperTech Metals Inc. This move is intended to bolster US copper security and advance technology and infrastructure transformation, potentially benefiting from increased US government support.
CopperTech Metals will own and operate the Zambian mines, with Vedanta planning to raise an additional $1.5 billion to boost copper production from an estimated 140,000 tonnes in 2026 to 300,000 tonnes by 2031. Funding options for the $1.5 billion are being explored, including a potential public listing of CopperTech Metals.
On 7th November, the US Department of the Interior added copper to its list of critical minerals. Other additions include Boron, Lead, Metallurgical coal, Potash, Rhenium, Silver, Silicon, and Uranium. The updated list will influence federal investments and permitting decisions aimed at securing domestic supply chains.
Oil & Gas
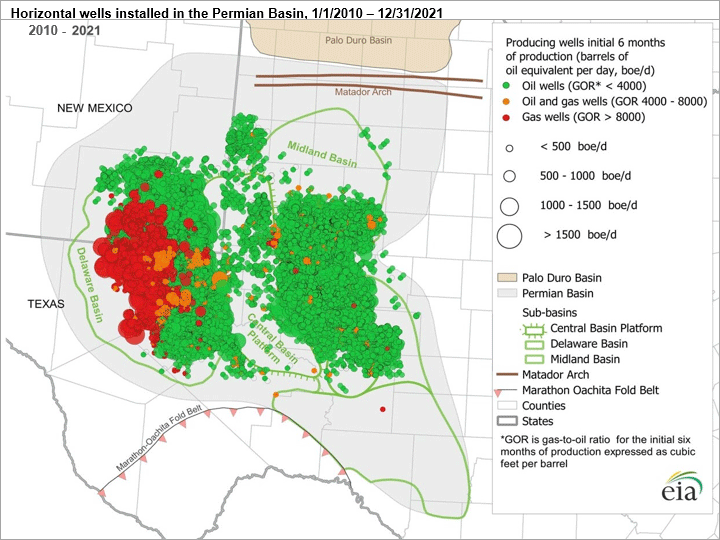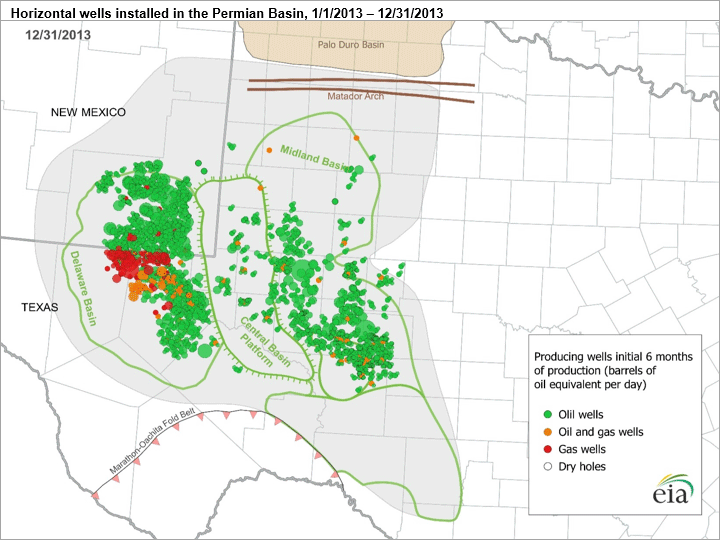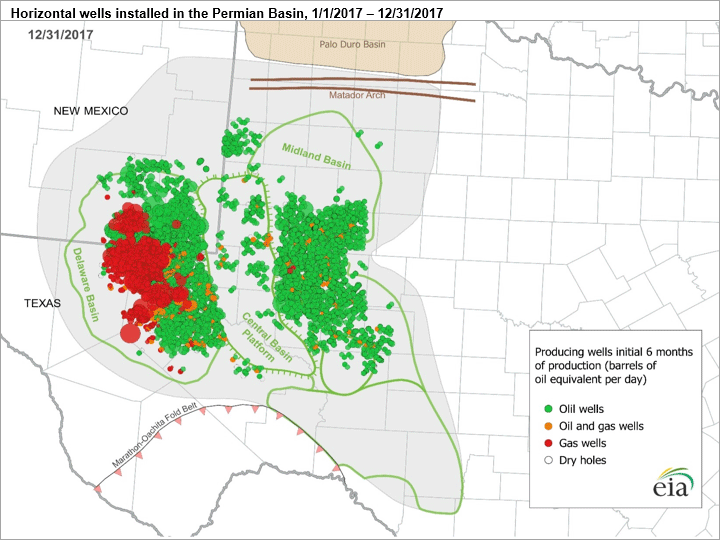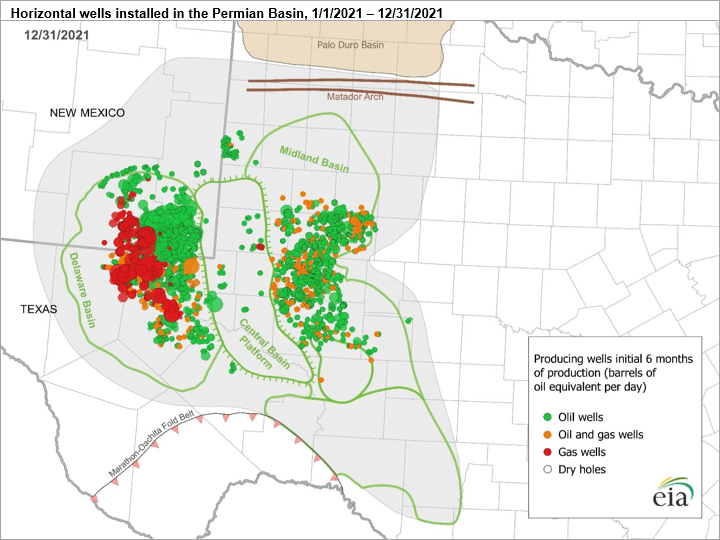
SM Energy and Civitas Resources are combining in a $12.8 billion merger. This deal will create a major oil and gas producer focused on the Permian Basin and one of the top 10 independent oil producers in the US. The combined company will retain the SM Energy name and will possess over 800,000 acres in key Permian Basin shale basins. Consolidation among Permian Basin oil producers is occurring to achieve greater scale. The deal is expected to be finalized in the first quarter of next year, pending regulatory approval.
Post the announcement of the above merger, BP announced its agreement to sell US midstream assets (infrastructure and facilities for the storage, processing, and transportation of petroleum products like oil and natural gas) to Sixth Street, a global investment firm headquartered in San Francisco, for $1.5 billion. This transaction is part of BP's strategy to unlock capital from its infrastructure and reduce net debt. The sale is expected to make a significant contribution towards BP's divestment targets, which includes raising $20 billion by 2027.
Energy
Apollo Global Management has committed $6.5 billion to Ørsted's Hornsea 3 offshore wind project in the UK. The investment includes the acquisition price for a 50% interest in the joint venture that holds Hornsea 3, which is described as the world's largest offshore wind project, located 160 km off the Yorkshire coast. The project is scheduled for completion around the end of 2027. Apollo has been active in the European energy infrastructure, investing in Germany's electricity grid and financing the Hinkley Point C nuclear power plant in the UK.
Pharma
Pfizer has won a $10 billion deal to acquire Metsera, an obesity drug developer. This acquisition concluded a bidding war between Pfizer and Novo Nordisk. Novo had initially made an unsolicited bid for Metsera, which sparked a rival offer from Pfizer. The competition escalated, with Novo increasing its offer to up to $10 billion, surpassing its previous bid of up to $9 billion. Metsera cited
"unacceptably high legal and regulatory risks"
associated with Novo's bid as a reason for accepting Pfizer's offer.

