TCL#36: The Rewiring
Bets on batteries and AI while oil titans stumble
While America's research institutions forge new alliances, Argonne with UT Dallas and Cornell receiving its AI materials windfall, the old industrial titans stumble through earnings like giants walking on shifting ground.
The battery revolution marches forward relentlessly. From Aachen's recycling laboratories to Charlotte's coating facilities, lithium has become the new oil: coveted, contested, and increasingly recyclable. Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) projects sprout like federally-funded seedlings, while Houston's Solidec promises to revolutionize chemical manufacturing with nothing but air, water, and electricity.
Yet even as these green shoots emerge, yesterday's certainties become today's anxieties. Dow slashes its dividend, and Chevron's earnings deflate by 43%.The wheel of industrial fortune spins with characteristic indifference, rewarding the nimble while punishing the complacent.
Materials
- Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) and The University of Texas at Dallas (UT Dallas) are collaborating to strengthen battery innovation and secure critical materials supply chains in the United States. The partnership aims to enhance the connection between the two institutions and foster scientific breakthroughs in areas critical to U.S. competitiveness and national security. Researchers from Argonne's Advanced Energy Technologies (AET) directorate and UT Dallas's Batteries and Energy to Advance Commercialization and National Security (BEACONS) Center will collaborate. BEACONS was established in 2023 with a $30 million award from the U.S. Department of Defense to drive energy storage solutions for researchers and industry partners.
- The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), in partnership with Intel, is investing $20 million over 5 years to establish the Artificial Intelligence Materials Institute (AI-MI) at Cornell University. The institute aims to accelerate the discovery of new materials for use in sustainable energy, advanced electronics, and quantum technologies, and to harness the rising tide of materials data using AI to enable scientists to develop new materials based on prediction.
Battery
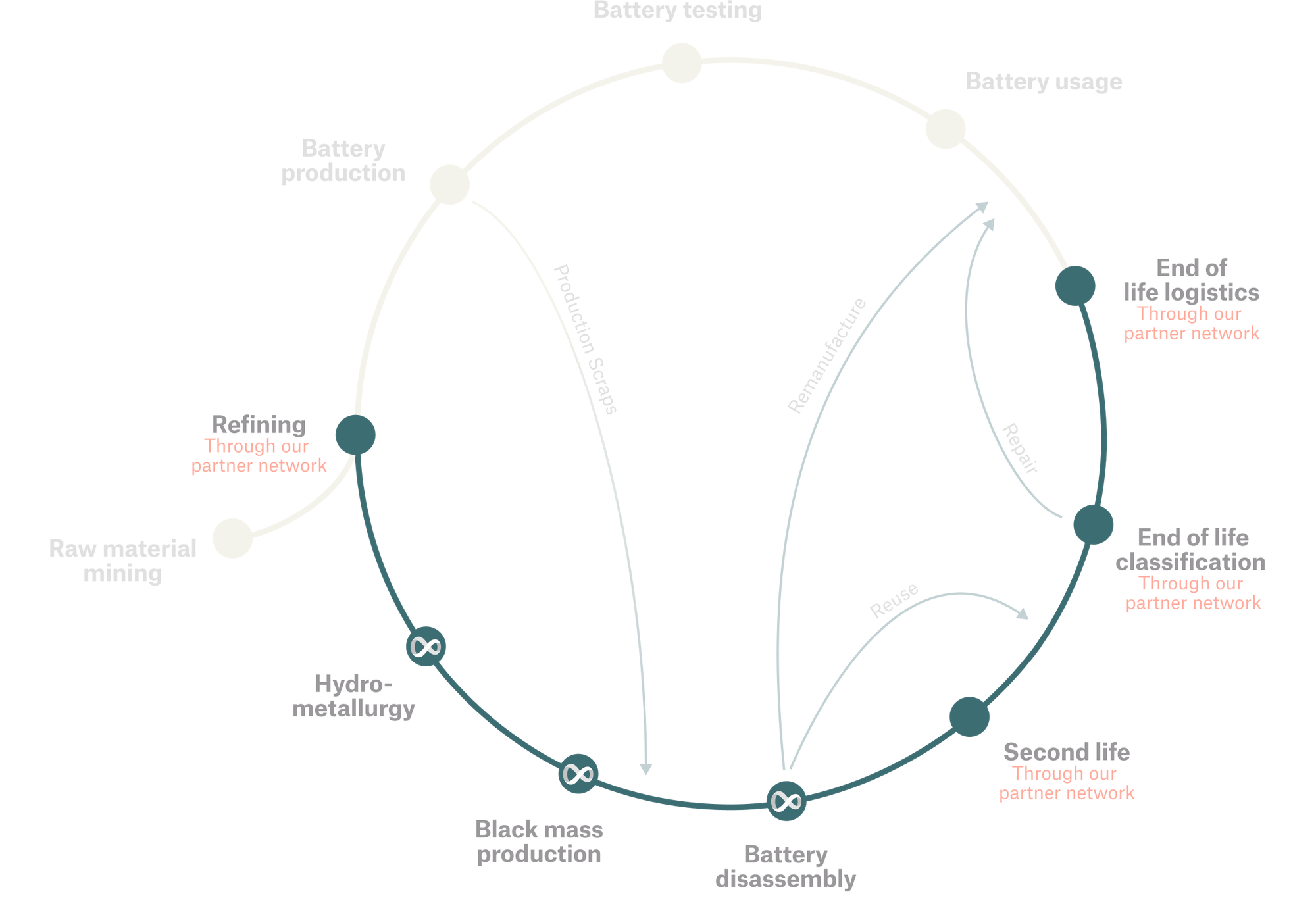
- cylib, a battery recycling company founded in 2022 in Aachen, Germany, and Syensqo have produced high-purity lithium hydroxide from spent electric vehicle (EV) batteries. This feat is the first in the battery recycling industry to extract and purify lithium from shredded battery electrodes from different battery chemistries on a single operating line. The process uses CYANEX 936P, a phosphorous-based extractant designed for lithium extraction, that selectively forms a complex with lithium at any lithium concentration. This milestone aligns with the European Union's battery recycling objectives, which mandate recovering at least 50% of lithium content by 2027 and 80% by 2031.
- Asahi Kasei and Toyota Tsusho have formed a strategic partnership to ensure a reliable supply of lithium-ion battery (LIB) separators in North America. Toyota Tsusho is a member of the Toyota Group and functions as a trading company that supports the global operations of Toyota Group companies. Asahi Kasei Battery Separator America, LLC (AKBSA) will supply Toyota Tsusho America, Inc. (TAI) with Hipore (a microporous polyolefin sheet) wet-process LIB separator starting mid-2027. The supply will come from a new coating facility under construction in Charlotte, North Carolina. Asahi Kasei is also advancing plans to establish a battery separator facility in Canada.
Aviation Fuel
GranBio LLC, a Brazilian industrial biotechnology company that creates solutions to transform biomass into renewable products, and Rayonier Advanced Materials Inc. (RYAM) are set to explore the development of a small-scale commercial cellulosic SAF project at RYAM's Jesup, Georgia facility. GranBio will lead the project, using its proprietary AVAP technology to convert lignocellulosic biomass into second-generation ethanol, which will be upgraded into SAF for sale. The new facility will leverage RYAM's existing infrastructure, including feedstock, utilities, and logistics, and will be partially financed through a $100 million grant from the U.S. Department of Energy.
Manufacturing
Solidec, a clean chemical manufacturing company based in Houston, TX, raised over $2 million in pre-seed funding. Solidec's platform can produce chemicals inluding hydrogen peroxide, formic acid, acetic acid, and ethylene, without any post-processing steps. The company's platform replaces centralized infrastructure with modular, on-site production using only air, water, and electricity.
Earnings
- Dow Inc. reported a Q2 2025 net loss of $801 million, compared to a $458 million profit in the same quarter last year. Quarterly sales fell 7% to $10.1 billion, down from $10.9 billion a year earlier. The company cut its dividend by 50%.
- For Q2 2025, ExxonMobil reported earnings of $7.1 billion, which translates to $1.64 per share after dilution. Shareholder distributions totaled $9.2 billion, including $4.3 billion in dividends and $5.0 billion in share repurchases. Year-to-date earnings were $14.8 billion, with advantaged volume growth in the Permian and Guyana, additional structural cost savings, and favorable timing effects partially offsetting lower earnings due to weaker crude prices and industry refining margins.
- Chevron reported Q2 2025 earnings of $2.5 billion, or $1.45 per diluted share. This is a 43% decrease from Q2 2024, when earnings were $4.4 billion, or $2.43 per diluted share. The company's adjusted earnings were $3.1 billion, a 34% decline from the same period in 2024. Chevron returned $5.5. billion to shareholders, including $2.6 billion in share repurchases and $2.9 billion in dividends.

